Supply Chain Lead Time
and It’s Impact on
Performance
Picture a seamless supply chain where every cog turns with precision, minimizing uncertainty and maximizing success. This is the goal, yet lead time variability remains a formidable obstacle. In the realm of supply chain management, the impact of uncertain lead times ripples through key performance metrics, from bloated inventory costs to unwarranted carbon expenditures, delivery delays, and stockouts, not to mention wavering service levels. Since the factors causing longer lead times are multi-faceted, so are the solutions to overcome them.
What is Lead Time in Supply Chain?
Lead time in the supply chain is the duration between receiving an order (moving goods from manufacturer, warehouse, distributor, retailer, or supplier) and its delivery to the recipient. In supply chain management, lead time spans various stages, from production and procurement to shipment and distribution. It is crucial to understand lead times to improve inventory management, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Types of Lead Times
Manufacturing Lead Time
Lead time in manufacturing describes the amount required to transform raw materials into finished goods ready for distribution. This time encompasses order preparation time, wait time, setup time, production run time, quality testing time, material handling time, and transportation time. Accurate lead time in manufacturing drives operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved customer relationships.
Shipping Lead Time
Shipping lead time represents the time the supplier requires to deliver goods to the recipient from the point of origin to its final destination. This is a critical aspect of the supply chain as it helps companies to manage their production schedules, inventory controls, and demand forecasting.
Replenishment Lead Time
In supply chain management, replenishment lead time refers to the duration between placing an order (once replenishment is identified) and having the product available in inventory for use again. Adequate replenishment lead time minimizes the need to overstock inventory, ultimately reducing overhead costs.
Supplier Lead Time
Supplier lead time refers to the duration between an order received by a supplier and the shipment (can be partial) of that order. Managing supplier lead times effectively help companies achieve collaborative partnerships, customer service excellence, and overall competitiveness in the market.
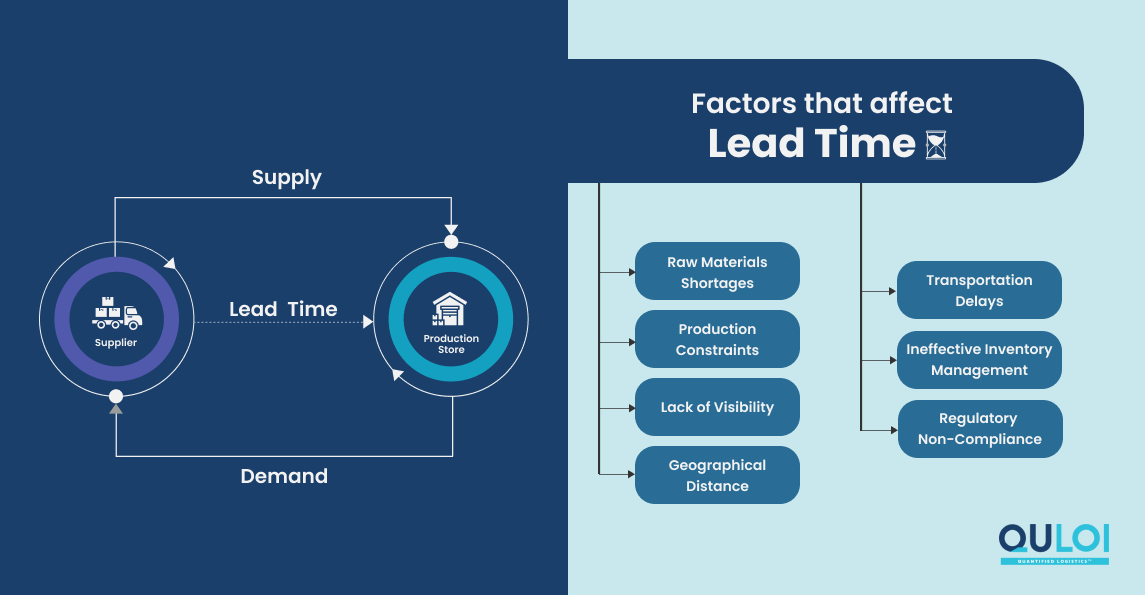
Causes of Longer Lead Times in Supply Chain
Raw materials shortages: With material shortages, manufacturers may not have the required inputs to produce finished goods. This can result in production delays, causing backlogs in orders and longer lead times- impacting the overall supply chain.
Production Constraints: Labor shortages, equipment breakdowns or maintenance, and inefficient processes cause a domino effect, leading to extended lead times. Additionally, high demand can overwhelm production capacity, causing delays in meeting fluctuating demand and resulting in longer lead times.
Lack of Visibility: When real-time information about production schedules, inventory levels, and shipments isn’t readily available, it becomes challenging to align these activities in a coordinated manner. A Deloitte study claimed that 40% of supply chain companies identified late delivery as their biggest problem. Delays in one part of the supply chain result in miscommunication, delays, and ultimately longer lead times.
Geographical Distance: When supply chain stakeholders locate in different areas, communication and coordination become challenging. Time zone differences and language barriers can affect problem-solving processes and decision-making, thereby extending lead time in the supply chain.
Transportation Delays: Transportation delays cause uncertainty in the goods to arrive at their intended destination. This uncertainty can disrupt the supply chain – affecting production schedules, inventory management, and customer expectations. The latest Deloitte research reveals that 53% of the surveyed companies report that supply chain disruptions have a strong to very strong impact on their business. Disruptions impact operational efficiency, causing longer lead times in supply chains.
Ineffective Inventory Management: With inadequate inventory management practices, there’s a higher likelihood of stockouts or excessive inventory levels. Stockouts mean customers must wait for the products to become available again, whereas excess inventory can become obsolete, occupying warehouse space and incurring storage costs. In 2022, eCommerce sellers lost almost $2 trillion to issues related to mismanaged inventory. 28% of companies surveyed experienced inventory shortages and looked for alternate sources of supply. Lead times increase as a result of poor inventory management.
Impact of Longer Lead Times on Supply Chain
Higher Bullwhip Effect: Longer lead times make the bullwhip effect worse. This happens when an irregular customer demand pattern impacts the product supply, resulting in a chain reaction involving manufacturers, suppliers, and wholesalers. As a result, production planning and procurement processes suffer inefficiencies – causing shipment delays and leading to revenue loss.
Increased Inventory Levels: The longer the lead times, the higher inventory levels are required to buffer against demand and supply gaps. This increases storage and holding costs, straining a company’s budget.
Inaccurate forecasting: Without measuring lead times, accurate demand forecasting becomes a challenge. Companies might produce goods based on inaccurate forecasts, resulting in stockouts or excess inventory. A study performed by Duc, T.T.H.; Luong, H.T.; Kim, Y.D. claimed forecasting inaccuracy is one of the main factors that weaken supply chain performance, leading to either excess inventory or shortages in the supply chain network. This causes operational inefficiencies and financial losses.
Reduced Agility: Usually, the longer the lead time, the harder it becomes for companies to respond to market changes quickly. When companies fail to adjust to their production schedules or cannot adapt to evolving market trends, it reduces agility. As a result, companies cannot navigate unexpected challenges or miss out on capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
How to Calculate Lead Time
Supply chain lead time can vary based on supply chains, warehousing, quality controls, etc. Here is a simple formula to calculate your supply chain lead time easily:
Supply Chain Lead Time = Manufacturing Lead Time + Procurement Lead Time + Transit Lead Time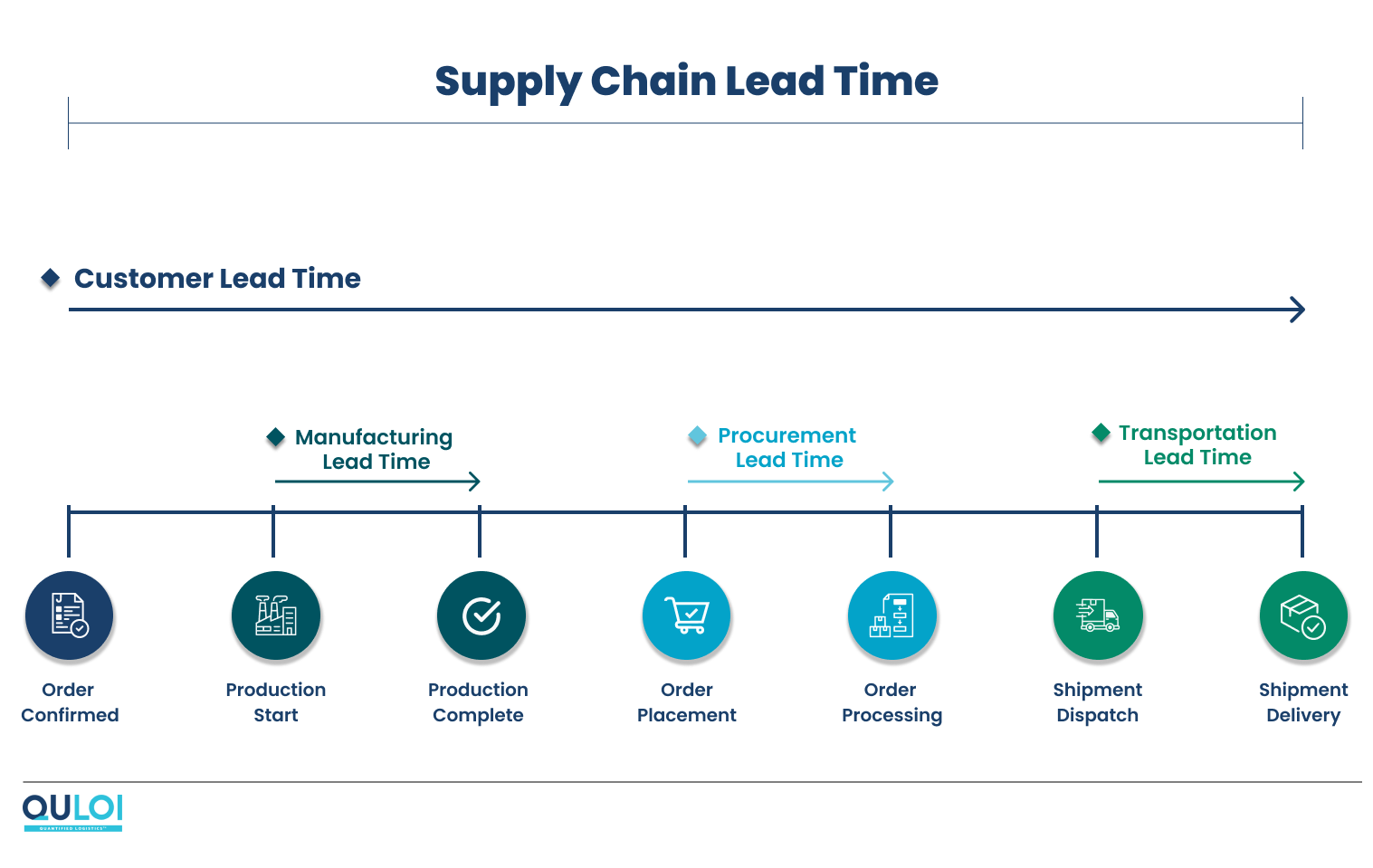
How to Reduce Lead Time in Supply Chain
Streamline Communication: Encourage supplier collaboration and modern communication tools to align production schedules, quality standards, and delivery timelines. Create a centralized repository that provides a single source of truth to stay updated and make informed decisions.
Implement Automation and Digitalization: Automate order processing, inventory tracking, and data entry to reduce human errors and accelerate information flow across the supply chain network. According to supply chain industry research, 63% of organizations have tech solutions in place to track the success of their supply chains. Supply chain digitalization helps companies achieve optimized operational performance and ensures accurate lead-time projections to drive result-oriented outcomes.
Source Local Suppliers: Local sourcing makes communication easier due to shared languages, overlapping time zones, and cultural understanding. This can help you significantly reduce lead times, minimize delays, and increase operational efficiency,
Evaluate Supplier Performance: Research conducted by North Carolina State University investigated the impact of supplier evaluation on buyer-supplier relationships and suggested that supplier evaluation has a positive influence on an organization’s financial performance. Key factors that involve supplier evaluation include price, quality, delivery, responsiveness to inquiries, risk level, etc.
Increase Visibility and Transparency: With real-time visibility into supply chain operations, everyone has access to the same information to identify bottlenecks and resolve them accordingly. Consider Quloi’s tech-powered supply chain visibility software to track every move of your supply chain, eliminate inefficiencies, and enhance decision-making.
Time is Money. Save Both with QULOI
Quloi, an innovative-first mile, collaborative supply chain digital platform with a focus on optimized lead time accuracy, responds directly to the needs of manufacturers, suppliers, and freight forwarders. With lead time accuracy, accelerate your order-to-delivery cycles, optimize inventory, and cut operational costs. Boost customer satisfaction by fulfilling customer expectations in promised timelines.
You don’t want to leave your lead times to chance. Get in Touch with our experts to schedule a demo or learn more about how Quloi empowers your business with unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
FAQs
What is a non-value-added lead
time in the supply chain?
Non-value-added lead time is any time spent on a step in the production or manufacturing process that adds nothing (no value) to the finished product. This is an activity that customers would not be happy to spend on.